If you want to use a single query to replace multiple spaces with one on SQL Server, you can read the articles here http://www.sqlservercentral.com/articles/T-SQL/68378/
However, it's very simple in PostgreSQL by using Regular Expression
SELECT regexp_replace('This sentence contains multiple spaces', '\s+', ' ', 'g');
Tuesday, January 1, 2013
PostgreSQL: Replace multiple spaces with one
Labels: DBA Tasks, PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL Query, PostgreSQL Tip
Sunday, December 30, 2012
PostgreSQL - Copy CSV to table with psql - part 2
CREATE TABLE tbl_test ( a text, b text, c text )Content of test.csv, and it put in /Database folder
a1,b1,c1
a2,b2,c2
a3,b3,c3
Instead of using COPY command directly, you can modify the test.cvs file to include it, as
COPY tbl_test FROM STDIN WITH CSV;
a1,b1,c1
a2,b2,c2
a3,b3,c3
\.
Note that you have to include a carriage return in the last line of the file (after '\.')
Then, run the following command to import
MyComputer$ psql -h localhost -p 5432 -U postgres testdb -f ~/Database/test.csv
Labels: DBA Tasks, PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL Query, PostgreSQL Tip
Thursday, December 13, 2012
PostgreSQL - Copy database
Sometimes, instead of back up and restore to a new db and wait your time if you only want to copy a database and put in the same server, you can use the following query:
CREATE DATABASE newdb WITH TEMPLATE originaldb OWNER dbuser;Note that this query only successfully if no sessions existing in originaldb. So, you can check originaldb sessions and kill them with this function pg_terminate_backend(procpid)
Labels: Backup, DBA Tasks, PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL Query, PostgreSQL Tip
PostgreSQL - Kill idle processes
Sometimes, you need to kill all unnecessary processes running on your database server. You can do that by using the following query:
SELECT procpid, ( SELECT pg_terminate_backend(procpid) ) AS killed FROM pg_stat_activity WHERE current_query LIKE '%idle%' AND datname = 'YourDBName';
Labels: DBA Tasks, PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL Query, PostgreSQL Tip
Sunday, December 9, 2012
PostgreSQL - Copy csv file to table with psql
CREATE TABLE tbl_test ( a text, b text, c text )Content of test.csv
a1,b1,c1
a2,b2,c2
a3,b3,c3
psql to COPY
psql -h localhost -U postgres testdb
testdb=# COPY tbl_test FROM 'D:\Temp\test.csv' WITH DELIMITER ',' CSV;
Labels: PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL Query, PostgreSQL Tip, psql
PostgreSQL - VACUUM ANALYZE EXPLAIN NOTIFY
Select the correct statement that records the space occupied by deleted or updated rows for later reuse, and also updates statistics.
A. VACUUM
B. VACUUM ANALYZE
C. EXPLAIN
D. EXPLAIN ANALYZE
E. NOTIFY
F. None of the above
Answer: [B]
Highlight to find out the answer.
Labels: PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL Query, PostgreSQL Quiz, PostgreSQL Tip
PostgreSQL - ANALYZE quiz
What does the following command do?
Choose the correct answer below.
Note: "psql=#" is the command prompt for psql.
psql=# ANALYZE xyz;
A. Collects statistical information related to the content of the database xyz.
B. Collects statistical information related to the content of the table xyz.
C. Outputs statistical information related to the content of the table xyz.
D. No ANALYZE command in PostgreSQL, error will occur.
E. None of the above
F. Both B & C
Answer: [B]
Highlight to find out the answer.
Labels: PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL Query, PostgreSQL Quiz, PostgreSQL Tip
Friday, December 7, 2012
PostgreSQL – Convert rows to string
SELECT array_to_string( array( SELECT name FROM pg_settings WHERE setting = 'off' AND context = 'postmaster' ), ','); SELECT setting, array_to_string(array_agg(name), ',') FROM pg_settings WHERE setting IN ('on', 'off') GROUP BY setting;
Labels: PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL Query, PostgreSQL Tip
Saturday, November 24, 2012
PostgreSQL - Query data from another database/server
Assume that, you have two databases:
1. db1 with two schemas: public and sch1
2. db2 with two schemas: public and sch2
In PostgreSQL, you can access a table from a different schema by using SELECT * FROM schema_name.table_name such as SELECT * FROM db1_sch.employee;
However, you cannot access a table on the different database with explicit way like SELECT * FROM db2.sch2.employee;
The question is how can we access like SQL Server or some other DBMS.
Fortunately, PostgreSQL support dblink to do that.
First, install extension dblink on the database you want to be able to access to other
CREATE EXTENSION dblink;
If db2 is in the same server, you can query table in db2 like that:
SELECT *
FROM dblink('dbname=db2', 'SELECT employee_id, employee_name FROM sch2.employee')
AS employee(employee_id integer, employee_name text);
If db2 is in the different server, you can query:
SELECT *
FROM dblink('hostaddr=172.x.x.x dbname=db2 user=admin password=pwd port=5432', 'SELECT employee_id, employee_name FROM sch2.employee')
AS employee(employee_id integer, employee_name text);
Labels: DBA Tasks, PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL Query, PostgreSQL Tip
Monday, November 5, 2012
PostgreSQL - get table structure
SELECT ordinal_position
, column_name
, CASE data_type WHEN 'character varying' THEN data_type || '('||character_maximum_length || ')' ELSE data_type END data_type
, column_default
, is_nullable
, character_maximum_length
, numeric_precision
FROM information_schema.columns
WHERE table_catalog = 'database_name'
AND table_schema = 'schema_name'
AND table_name = 'table_name'
ORDER BY ordinal_position;
Labels: DBA Tasks, PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL Query, PostgreSQL Tip
Friday, October 19, 2012
PostgreSQL: check the core settings of server
SELECT name, context, unit, setting, short_desc
FROM pg_settings
WHERE name in ('listen_addresses' ,'max_connections' ,'shared_buffers' ,'effective_cache_size' , 'work_mem' , 'maintenance_work_mem')
ORDER BY context,name;
If context is set to postmaster, it means changing this parameter requires a restart of the postgresql service. If context is set to user, changes require at least a reload. Furthermore, these settings can be overridden at the database, user, session, or function levels.
unit tells you the unit of measurement that the setting is reported in. This is very important for memory settings since, as you can see, some are reported in 8 kB and some in kB
Labels: DBA Tasks, PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL Query, PostgreSQL Tip
Thursday, October 18, 2012
PosgreSQL: get main configuration files
SELECT name, setting FROM pg_settings WHERE category = 'File Locations';
postgresql.conf controls general settings, such as how much memory to allocate, default storage location for new databases, which IPs PostgreSQL listens on, where logs are stored, and so forth.
pg_hba.conf controls security. It manages access to the server, dictating which users can login into which databases, which IPs or groups of IPs are permitted to connect and the authentication scheme expected.
pg_ident.conf is the mapping file that maps an authenticated OS login to a PostgreSQL user. This file is used less often, but allows you to map a server account to a PostgreSQL account. For example, people sometimes map the OS root account to the postgre’s super user account. Each authentication line in pg_hba.conf can use a different pg_ident.conf file
Labels: DBA Tasks, PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL Tip, SQL Tips
Wednesday, October 17, 2012
PostgreSQL quiz: stored procedure execution
Assume that you have a table contact and a stored procedure called insert_contact as the following screenshots
Which one below is correct?
A. CALL insert_contact(‘John’,'Tran’);
B. EXECUTE insert_contact(‘John’,’Tran’);
C. SELECT insert_contact(‘John’,’Tran’)
D. Both A & B
E. Error in the store procedure code
F. None of the above
Answer: [C]
Highlight to find out the answer.
Labels: PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL Quiz, PostgreSQL Tip, Quiz
Tuesday, October 16, 2012
PostgreSQL license
Select the most suitable statement about the PostgreSQL license from below.
A. PostgreSQL is distributed under the GPL license.
B. PostgreSQL is distributed under the PostgreSQL license.
C. PostgreSQL is distributed under the LGPL license.
D. PostgreSQL is distributed under the BSD license.
E. PostgreSQL is distributed under the X11(MIT) license.
Answer: [D]
Highlight to find out the answer.
Labels: PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL Quiz, PostgreSQL Tip, Quiz
Monday, October 15, 2012
Convert date time values to string in PostgreSQL
This is a view extracted from OpenERP.
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW crm_claim_report
AS
SELECT min(c.id) AS id
, to_char(c.date, 'YYYY'::text) AS name
, to_char(c.date, 'MM'::text) AS month
, to_char(c.date, 'YYYY-MM-DD'::text) AS day
, to_char(c.date_closed, 'YYYY-MM-DD'::text) AS date_closed
, to_char(c.date_deadline::timestamp with time zone, 'YYYY-MM-DD'::text) AS date_deadline, c.state, c.user_id
, c.stage_id, c.section_id, c.partner_id, c.company_id, c.categ_id, count(*) AS nbr, c.priority
, c.type_action, date_trunc('day'::text, c.create_date) AS create_date
, avg(date_part('epoch'::text, c.date_closed - c.create_date)) / (3600 * 24)::double precision AS delay_close
, ( SELECT count(mailgate_message.id) AS count FROM mailgate_message
WHERE mailgate_message.model::text = 'crm.claim'::text AND mailgate_message.res_id = c.id AND mailgate_message.history = true) AS email
, ( SELECT avg(crm_case_stage.probability) AS avg FROM crm_case_stage
WHERE crm_case_stage.type::text = 'claim'::text AND crm_case_stage.id = c.stage_id) AS probability
, date_part('epoch'::text, c.date_deadline::timestamp without time zone - c.date_closed) / (3600 * 24)::double precision AS delay_expected
FROM crm_claim c
GROUP BY to_char(c.date, 'YYYY'::text), to_char(c.date, 'MM'::text), to_char(c.date, 'YYYY-MM-DD'::text), c.state, c.user_id, c.section_id
, c.stage_id, c.categ_id, c.partner_id, c.company_id, c.create_date, c.priority, c.type_action, c.date_deadline, c.date_closed, c.id;
Labels: OpenERP, OpenERP:CRM, PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL Tip
Sunday, October 14, 2012
PostgreSQL Contactenation
Which query is correct in PostgreSQL?
A. SELECT 'Test' . 'query';
B. SELECT cat('Test','query') FROM dual;
C. SELECT 'Test' + 'query';
D. SELECT 'Test' + 'query' FROM dual;
E. SELECT 'Test' || 'query';
Answer:[E]
Highlight to find out the answer.
Labels: PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL Quiz, Quiz
Tuesday, October 9, 2012
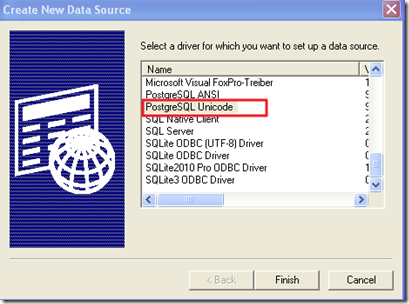
Create SQL Server linked server to PostgreSQL database
1. Download ODBC Driver at this address http://www.postgresql.org/ftp/odbc/versions/msi/
Choose the suitable version with your PostgreSQL database. I’m using PostgreSQL 9, so I chose latest version. (^_^)
2. Install ODBC Driver for PostgreSQL
3. Create connection to PostgreSQL database with ODBC Driver
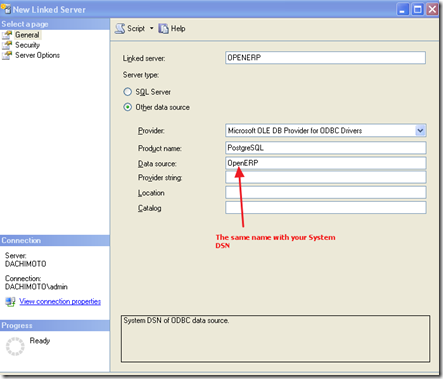
4. Now, it’s time to create linked server to PostgreSQL database:
You can create with GUI
Or can create with scripts
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'OPENERP', @srvproduct=N'PostgreSQL', @provider=N'MSDASQL', @datasrc=N'OpenERP';
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedsrvlogin @rmtsrvname=N'OPENERP',@useself=N'False',@locallogin=NULL,@rmtuser=NULL,@rmtpassword=NULL;
GO
Finally, you can query PostgreSQL database inside SQL Server
5. Verify the linked server
Monday, October 8, 2012
Get current queries executing on PostgreSQL
SELECT datname "Database Name"
, usename "User Name"
, procpid "Process ID"
, client_addr "Client IP Address"
, waiting "Is waiting"
, query_start "Start Time"
, current_query "Query Text"
FROM pg_stat_activity;
Labels: DBA Tasks, PostgreSQL, SQL Tips
Friday, October 5, 2012
Saturday, September 29, 2012
Inspecting your postgreSQL connection information
If you want to confirm you've connected to the right place and in the right way, you can execute some or all of the following commands:
SELECT inet_server_port();
SELECT current_database();
SELECT current_user;
SELECT inet_server_addr();
SELECT version();
Labels: DBA Tasks, PostgreSQL